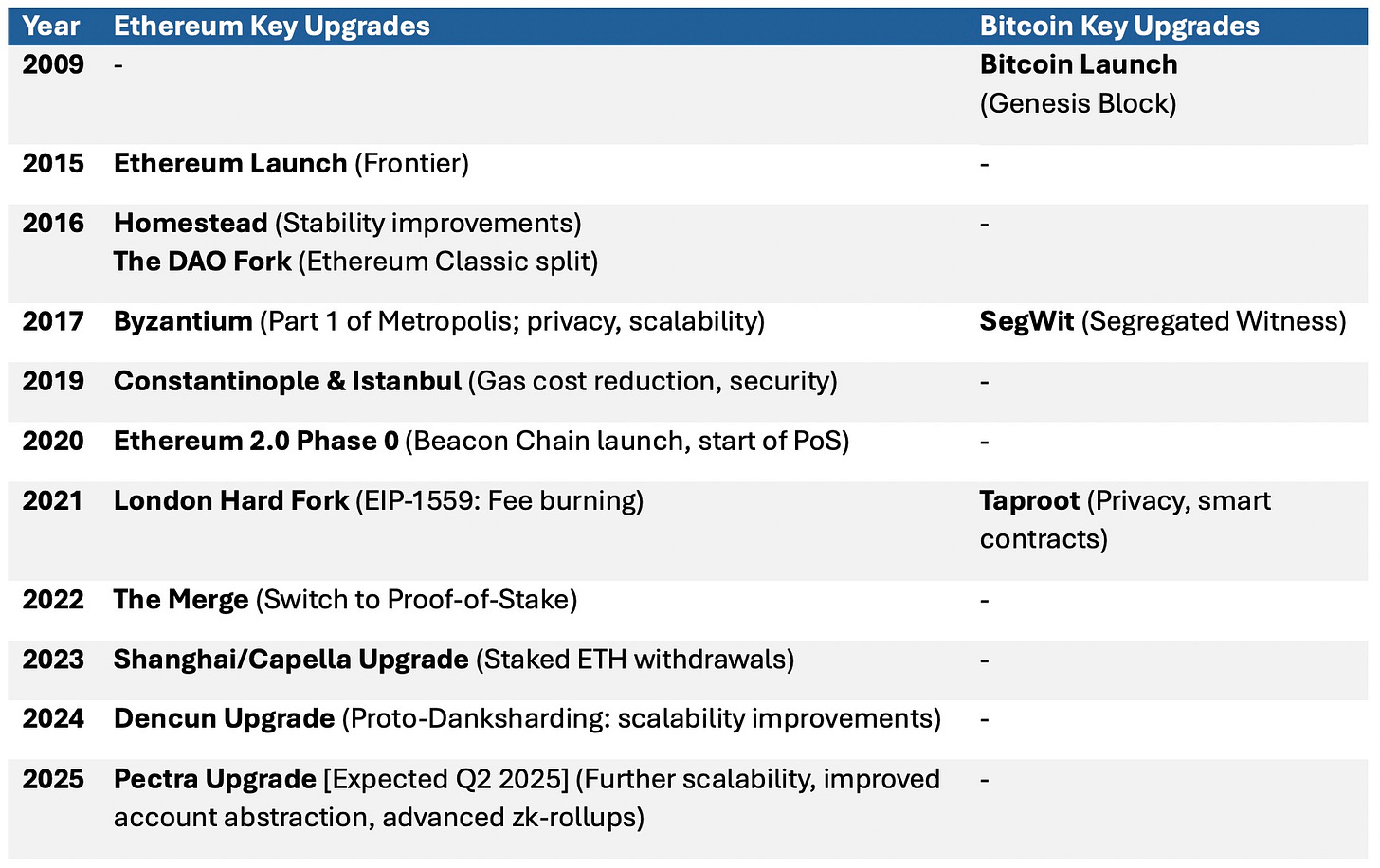
Ethereum is a constantly improving technology.
Unlike Bitcoin, whose holders love it’s simplicity and hardcap, Ethereum has added hundreds of Ethereum Improvement Protocols (EIPs) since inception in an effort to improve the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
EIP 1 showed the design document for the EIPs to be included in the Ethereum Protocol. It was released in October 2015, two months after the Genesis Block.
Anyone can submit an EIP but it must gain community support to be included in hard fork upgrades. The next upgrade, Pectra, is scheduled to go live May 7th 2025. It will be one of the largest upgrades to the EVM since inception.
Why are EIPs important?
EIPs are important because it allows the EVM infrastructure to constantly improve, similar to IOS updates on the iPhone. These updates are based on:
New research / technology
Changing market conditions - introduction of Proof-of-Stake, increased fee markets
Market demand - increased blob count for Layer 2s
Notable EIPs improving the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
EIP-20: Created the ERC-20 standard which most tokens use today. ERC-20 is a standard API between smart contracts. Think of it as agreeing on the shape of the electrical outlet.
EIP-115: Changed to how Ethereum handles transactions so that people can't copy and reuse (replay) the same transaction on other EVM blockchains. It links a chain ID (e.g. 1 for Ethereum, 8453 for Base) to each transaction.
EIP-721: Helped create ERC-721, the NFT token standard.
EIP-1559: Fee market upgrade, allows smoother fee market spikes and burning of Ethereum to get included in next block.
EIP-3675: Transition from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake. Allowed Ethereum holders to generate yield via staking which provides economic security to the network.
EIPs in Pectra (Prague [execution layer] + Electra [consensus layer])
EIP-7702: Allows for normal addresses to act like smart contracts for a single transaction. It enables subsidizing user gas, reduces the need for multiple confirmations, and increases functionality of each onchain address. In my opinion, this will allow creativity to flourish as it gives developers a lot of flexibility moving forward on different ways to engage onchain wallets.

EIP-7251: Allows validators increase the max amount of ETH staked from 32 to 2048. This will improve the network by reducing operational needs of validators and enables compounding for smaller validators.
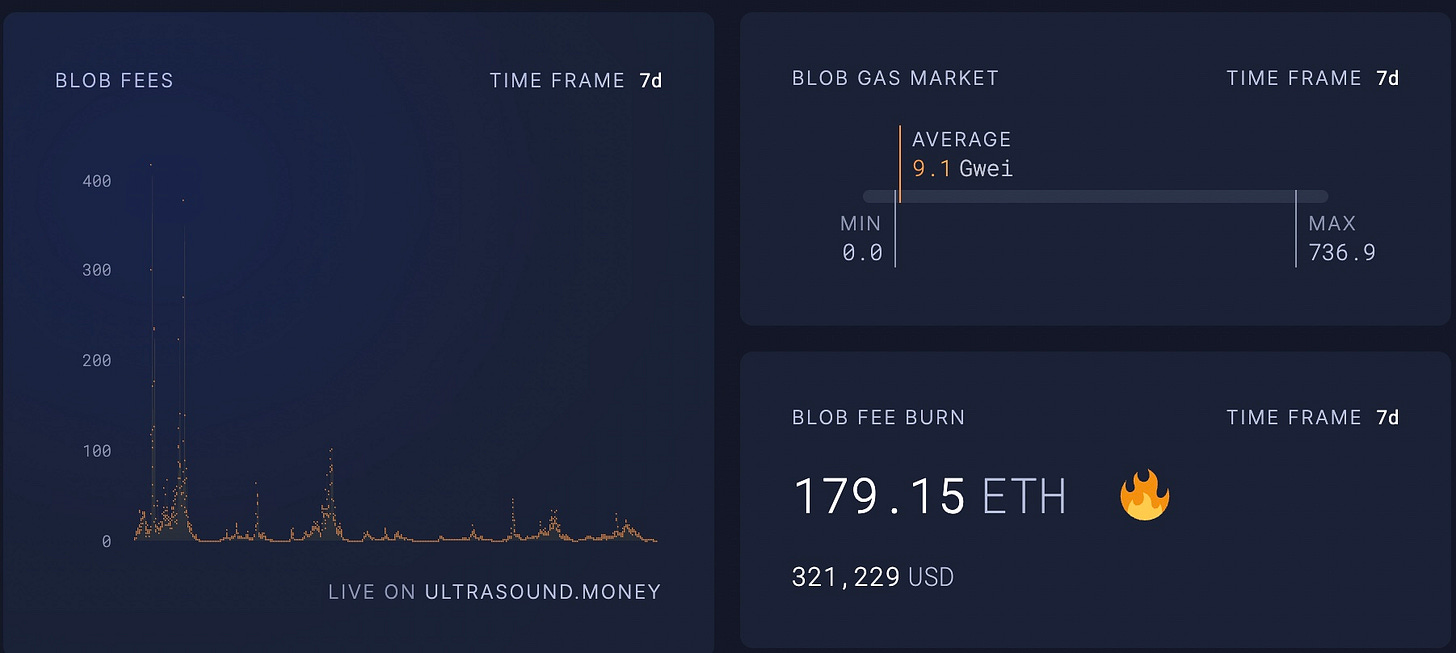
EIP-7691: Raises the target blob count per block from 3 to 6 and the max from 6 to 12, which provides more data availability for roll ups. This helps the L2 roadmap.
Additional EIPs include: EIP-7623, EIP-7002, EIP-7685, EIP-2537, EIP-2935, EIP-6110, EIP-7549, and EIP-7840.
Ethereum expects to have a network upgrade every 6-12 months moving forward. Post Pectra, the next upgrade for the EVM is called Fusaka. This will be centered around EIP-7594 or PeerDAS. It is expected in Q4 2025.
Hardfork timelines are set during Ethereum All Core Developer calls which happen every two weeks and alternate between execution layer and consensus layer. All of these decisions take place in public where anyone curious can watch and learn.
Innovating in public isn’t easy, neither is inventing the next great technology platform.
The future will be built on Ethereum.
Cheers,
Whitetail & Co